Measuring temperatures with a temperature sensor
Temperature sensors are electronic components and, as the name suggests, serve a single purpose: reading the ambient temperature. The sensor converts the measured values into an electrical signal.
We encounter temperature sensors in everyday life, for example, in kettles that measure the temperature of the water. When the desired temperature is reached, the kettle switches off.
Temperature measurement with a resistor
The most common analog or digital temperature sensors are so-called semiconductor temperature sensors. They work on the basis of a physical principle. A change in the electrical measured variable is achieved within the sensor as a function of the absolute applied temperature.
There is a resistor inside the temperature sensor. This resistance does not always react in the same way to changes in the ambient temperature, depending on the type of construction. We distinguish between hot conductors, where the resistance value decreases with an increase in temperature, and PTC thermistors, where the resistance value also increases with an increase in temperature.
The DS18B20 temperature sensor
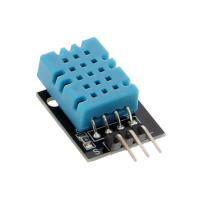
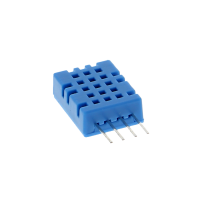
The most popular temperature sensor for Arduino and Raspberry Pi microcontrollers is the DS18B20. The sensor is, depending on the design, waterproof and impresses with a particularly high measurement accuracy. In addition, the DS18B20 stands out due to its 1-Wire interface: The interface enables communication between microcontroller and sensor via only one data line, the so-called "one-wire bus". This allows you to connect (almost) any number of DS18B20 temperature sensors to just one single single-board computer and process the data - only the maximum power capacity regulates the maximum number of DS18B20 sensors.
In our online store we offer two versions of the temperature sensor: as a "naked" sensor without sheathing and with 2.54mm pin headers and in a waterproof version for measuring the temperature of liquids. You are spoiled for choice!