Where are level converters used in microelectronics?
Often two devices or modules are to communicate with each other in electronic circuits. Even more often, these two modules require a different voltage level. In microelectronics, for example in an Arduino microcontroller, this voltage level is usually 3.3V or 5V. If one were to directly connect a module operating at 3.3V and a module operating at 5V, the module with a maximum operating voltage of 3.3V would be destroyed with a 5V level applied.
So that exactly this is avoided, one falls back to so-called level converters. Level converters allow the communication between two modules with different voltage levels. It is particularly interesting that level converters work in two directions without having to change anything on the connection. The signal can therefore be sent from one module to the other. Level converters are therefore also suitable for I2C lines. Furthermore it is possible to raise or lower the voltage level of switch inputs or switch outputs.
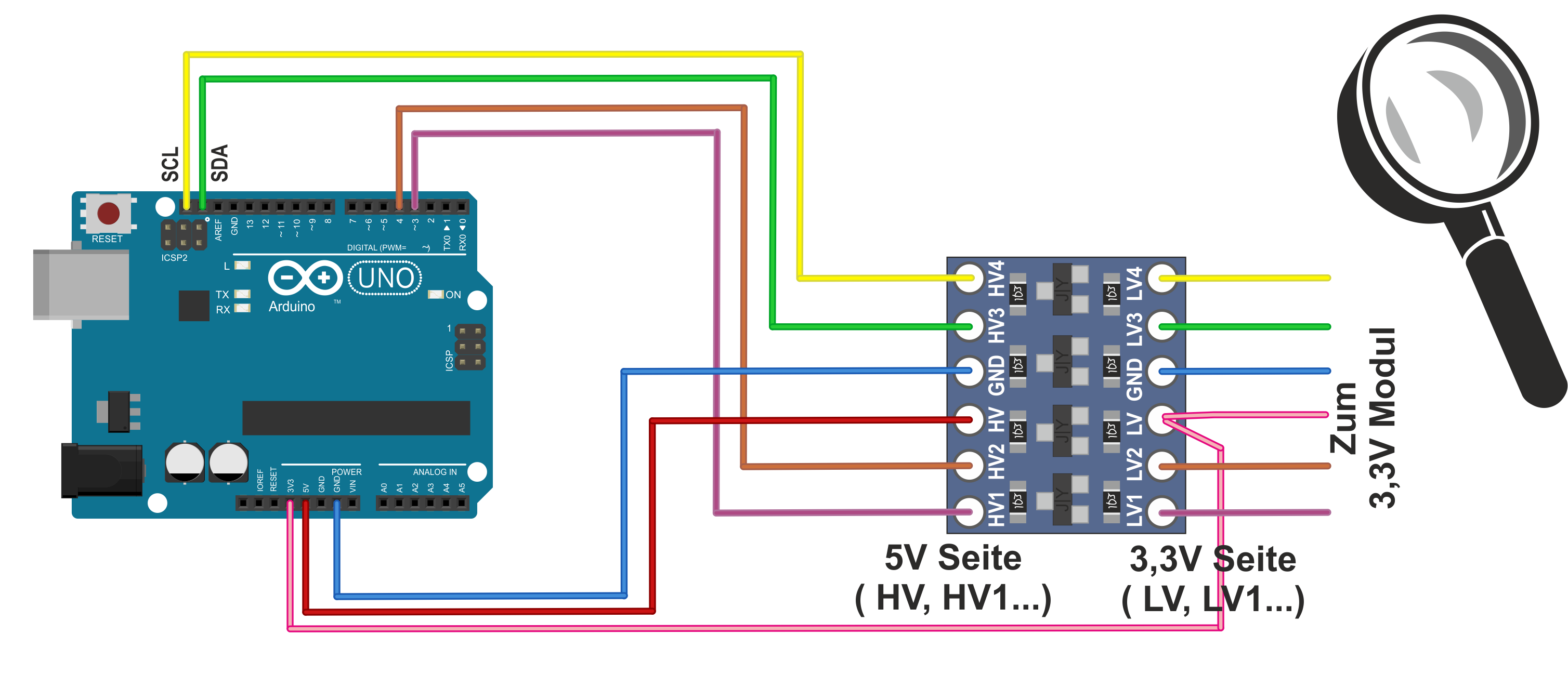
Level converters: How do they work?
The picture above shows very well how the signal transmission inside a level converter for 3.3 and 5V works. On the board, the 5V level (HV, "High Voltage") and the 3.3V level (LV, "Low Voltage") are directly opposite each other. It should be noted that the module used in this example (article is linked below) can only "switch" a few milliamps. The module is not suitable for switching motors or lamps, for example.