The breadboard - basis in microelectronics
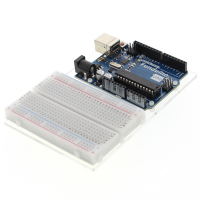
A breadboard is the central connecting element of your project and for programming with single board computers like the Arduino an indispensable tool for building simple electronic circuits.
The breadboard is composed of a plastic housing, which contains electronic contact surfaces in the form of conductor tracks inside. On the housing itself there are tiny holes, mostly in 2.54mm pitch.
If you want to connect a cable, a sensor or simple electronic components such as resistors to the breadboard, you simply insert it into the plug-in board. And this is exactly where the central added value of the breadboards becomes clear: no additional soldering work is required. Circuits can thus be assembled, disassembled and reconfigured in a matter of seconds. Breadboards are therefore indispensable for the construction of prototypes.
The different types of breadboards
Every breadboard is the same - right? Not quite, because the boards come in many sizes, colors and designs.

In the picture above you can see the typical design of a breadboard for microelectronics. The traces, which are located inside the board, are highlighted here. It is immediately noticeable that some traces are horizontal, but some are vertical.
The horizontal traces are for the power supply and the ground connection of the controller. They extend over the whole length of the board.
The vertical traces represent the "working area" of the plug-in board.
In the middle of this working area there is a bar. This bar separates the tracks to the right and left of it. This gives you twice the number of traces.