Bluetooth for microelectronics
In the course of digitalization, the integration of mobile devices such as smartphones or tablets into school lessons is playing an increasingly important role. And this trend is also becoming more and more common in microcontrolling projects at home.
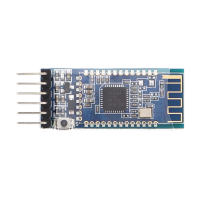
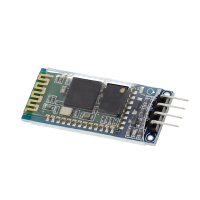
Bluetooth technology plays an overriding role here. It enables secure wireless communication between one or more Bluetooth-enabled devices. Since most microcontrollers are not directly Bluetooth-capable ex works, they have to be equipped with an additional module.
Here we distinguish between "master" and "slave" modules. These admittedly somewhat outdated terms are used to designate the hierarchical order within the communication of two Bluetooth interfaces. The "master" module is exclusively intended for sending signals, while the "slave" module takes the part of the receiver module. A special exception are "Master/Slave" modules, like the HC-05, which are able to send and receive signals.
How do I use the Bluetooth interface?
Thanks to great tools like MIT App Inventor, custom apps can be programmed in no time. In order for these apps to be able to communicate with the microcontroller, one falls back on the proven Bluetooth technology. The microcontroller (with a connected Bluetooth module) is paired with the mobile device. After establishing a successful Bluetooth connection, you can now send commands to the microcontroller via keystrokes on the end device without having to rely on an additional cable or WiFi connection.